使用其他LLM、ChromaDB为Microsoft SQL Server生成SQL
您想使用哪个LLM?
使用您自己的API密钥使用OpenAI
-
Azure OpenAI如果您在Azure上部署了OpenAI模型
-
通过La plateforme使用MistralAnthropic
-
使用您的Anthropic API密钥使用Anthropic的Claude在本地免费使用Ollama。需要额外设置。
-
GeminiGoogle Gemini
-
使用您的Gemini或Vertex API密钥使用Google Gemini通过Mistral API使用Mistral
-
如果您有Mistral API密钥[已选择] 其他LLM
-
如果您有不同的LLM模型您想在哪里存储“训练”数据?
[已选择] ChromaDB
-
在本地免费使用ChromaDB的开源向量数据库。无需额外设置——所有数据库文件将在本地创建和存储。使用Qdrant的开源向量数据库
-
Marqo在本地免费使用Marqo。需要额外设置。或使用其托管选项。
-
其他向量数据库其他向量数据库
-
使用任何其他向量数据库。需要额外设置。您想查询哪个数据库?
训练
%pip install 'vanna[chromadb]'
from vanna.base import VannaBase
from vanna.chromadb import ChromaDB_VectorStore
class MyCustomLLM(VannaBase):
def __init__(self, config=None):
# Implement here
pass
def submit_prompt(self, prompt, **kwargs) -> str:
# Implement here
# See an example implementation here: https://github.com/vanna-ai/vanna/blob/main/src/vanna/mistral/mistral.py
class MyVanna(ChromaDB_VectorStore, MyCustomLLM):
def __init__(self, config=None):
ChromaDB_VectorStore.__init__(self, config=config)
MyCustomLLM.__init__(self, config=config)
vn = MyVanna()
Postgres
-
[已选择] Microsoft SQL Server
-
使用Vanna为任何SQL数据库生成查询
-
Oracle
-
Microsoft SQL
-
BigQuery
-
SQLite
-
其他数据库
-
Snowflake
-
LLMs您只需要训练一次。除非您想添加更多训练数据,否则不要再次训练。
vn.connect_to_mssql(odbc_conn_str='DRIVER={ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server};SERVER=myserver;DATABASE=mydatabase;UID=myuser;PWD=mypassword') # You can use the ODBC connection string here
启动用户界面

# The information schema query may need some tweaking depending on your database. This is a good starting point.
df_information_schema = vn.run_sql("SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS")
# This will break up the information schema into bite-sized chunks that can be referenced by the LLM
plan = vn.get_training_plan_generic(df_information_schema)
plan
# If you like the plan, then uncomment this and run it to train
# vn.train(plan=plan)
# The following are methods for adding training data. Make sure you modify the examples to match your database.
# DDL statements are powerful because they specify table names, colume names, types, and potentially relationships
vn.train(ddl="""
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS my-table (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
age INT
)
""")
# Sometimes you may want to add documentation about your business terminology or definitions.
vn.train(documentation="Our business defines OTIF score as the percentage of orders that are delivered on time and in full")
# You can also add SQL queries to your training data. This is useful if you have some queries already laying around. You can just copy and paste those from your editor to begin generating new SQL.
vn.train(sql="SELECT * FROM my-table WHERE name = 'John Doe'")
# At any time you can inspect what training data the package is able to reference
training_data = vn.get_training_data()
training_data
# You can remove training data if there's obsolete/incorrect information.
vn.remove_training_data(id='1-ddl')
```## Asking the AI
Whenever you ask a new question, it will find the 10 most relevant pieces of training data and use it as part of the LLM prompt to generate the SQL.
```python
vn.ask(question=...)
本Notebook详细介绍了如何使用 vanna Python包通过AI(RAG + LLMs)生成SQL,包括连接数据库和训练。如果您还没有准备好在自己的数据库上进行训练,仍然可以使用示例 SQLite数据库 进行尝试。
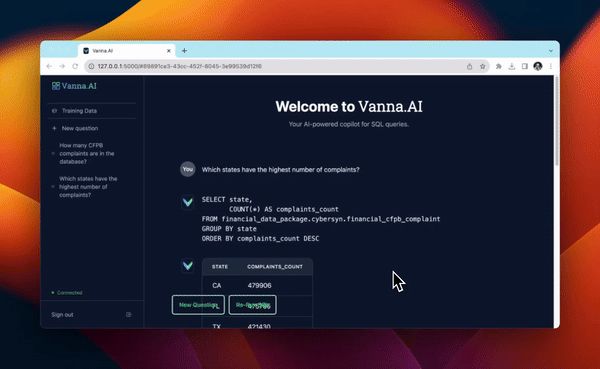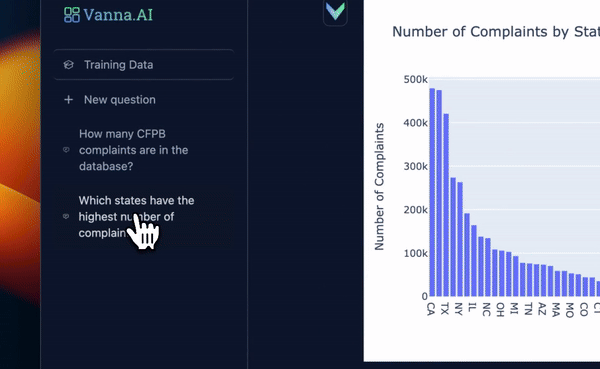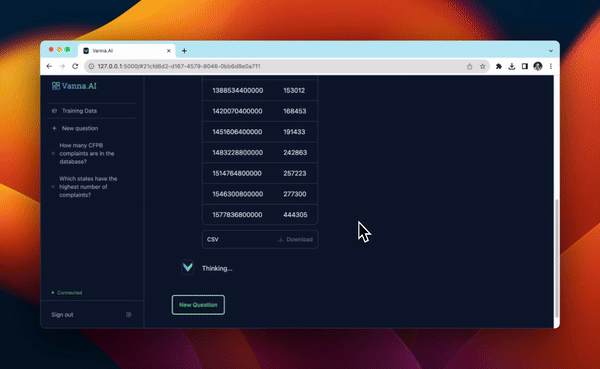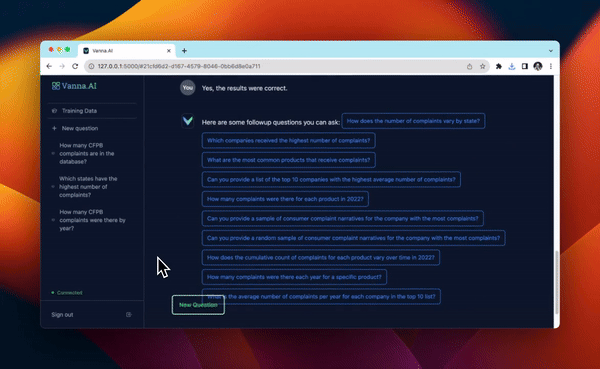
from vanna.flask import VannaFlaskApp
app = VannaFlaskApp(vn)
app.run()